Vapour Pressure – Definition, Factors & Uses
Vapour pressure is the pressure made by vapour when it is in balance with its liquid or solid form at a fixed temperature in a closed container. This property is important in colligative properties, thermodynamics, and solution chemistry.
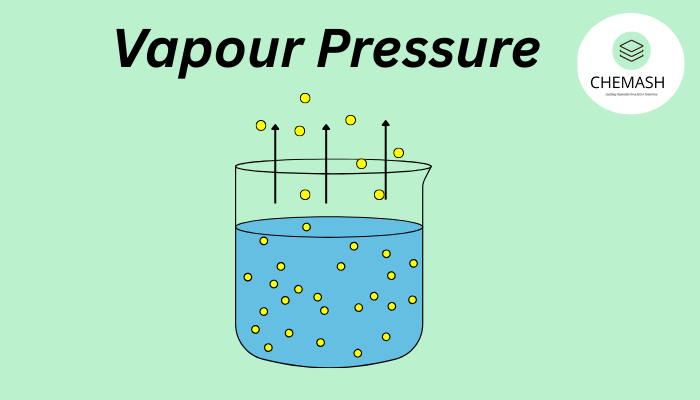
What Happens Inside?
In a closed container, some liquid molecules escape into the vapour phase. At the same time, some vapour molecules return to the liquid. When these two rates become equal, the system reaches dynamic equilibrium. The pressure at this point is called vapour pressure.
Factors That Change Vapour Pressure
- Temperature: Higher temperature → more molecular movement → higher vapour pressure.
- Type of Liquid: Volatile liquids (like ether) have high vapour pressure; non-volatile liquids (like water, glycerin) have low vapour pressure.
- Non-Volatile Solutes: Adding salt, sugar, or other non-volatile solutes lowers vapour pressure. This follows Raoult’s Law.
Raoult’s Law
In an ideal solution:
PA = XA × P0A
- PA = partial vapour pressure of A
- XA = mole fraction of A
- P0A = vapour pressure of pure A
Total vapour pressure: Ptotal = PA + PB
Lowering of Vapour Pressure
Adding a non-volatile solute lowers the solvent’s vapour pressure. Formula:
(P0 – P) / P0 = nsolute / (nsolute + nsolvent)
Uses of Vapour Pressure
- Boiling Point: Lower vapour pressure increases boiling point.
- Osmotic Pressure: Explains solvent movement through membranes.
- Medicine: Helps design drugs with correct evaporation rates.
- Food Packaging: Prevents moisture loss or gain in food.
- Perfumes: Controls how fast fragrance is released.
Conclusion: Vapour pressure connects the world of molecules with real-life uses. Understanding it is useful in science, industry, and everyday products.
MCQ Quiz – Test Your Knowledge
- Vapour pressure is measured when:
a) The liquid is boiling
b) The liquid and vapour are in equilibrium ✅
c) There is no evaporation
d) The vapour is moving fast - Which factor increases vapour pressure?
a) Lowering temperature
b) Increasing temperature ✅
c) Adding non-volatile solute
d) Reducing container size - Raoult’s Law applies to:
a) Real solutions
b) Ideal solutions ✅
c) Only gases
d) Only solids - Which liquid has the highest vapour pressure?
a) Water
b) Glycerin
c) Ether ✅
d) Mercury - Lower vapour pressure causes:
a) Lower boiling point
b) Higher boiling point ✅
c) No change
d) Faster evaporation
True / False Questions
- Adding a non-volatile solute increases vapour pressure. ❌ False – It lowers vapour pressure.
- Dynamic equilibrium means evaporation = condensation. ✅ True
- Vapour pressure decreases with temperature. ❌ False – It increases with temperature.
- Raoult’s Law uses mole fraction in its calculation. ✅ True
- Perfume evaporation is related to vapour pressure. ✅ True
