Aldol Condensation
Aldol Condensation is one of the most important reactions of aldehydes and ketones in organic chemistry. It is a high-weightage topic for Class 12 Board Exams and NEET.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Aldol Condensation
- Conditions Required
- Mechanism of Aldol Condensation
- Example of Aldol Condensation
- Dehydration Step
- Types of Aldol Condensation
- Aldol vs Crossed Aldol
- Limitations
- Exam Importance
- MCQs
- FAQs
- Reference Links
Definition
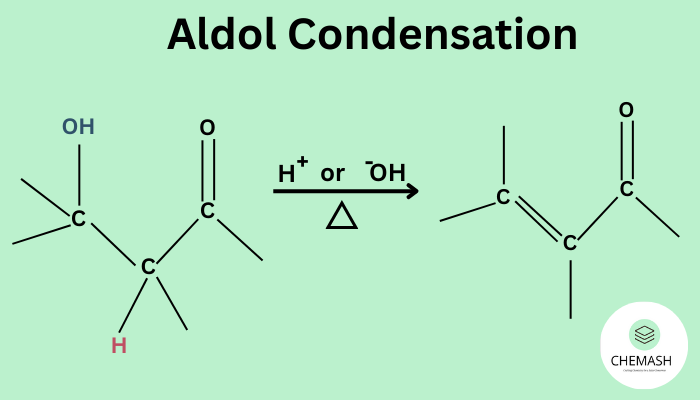
Aldol Condensations is a reaction in which aldehydes or ketones containing at least one α-hydrogen atom react in the presence of a dilute base to form β-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones (called aldols), which on heating dehydrate to give α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
The name “Aldol” is derived from aldehyde + alcohol.
Conditions Required for Aldol Condensations
- Presence of at least one α-hydrogen
- Dilute base like NaOH or KOH
- Aldehydes or ketones
Mechanism of Aldol Condensations
Step 1: Formation of Enolate Ion
The base abstracts an α-hydrogen forming a resonance-stabilized enolate ion.
Step 2: Nucleophilic Addition
The enolate ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of another molecule, forming a β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone.
Step 3: Dehydration
On heating, the aldol loses a molecule of water to form an α,β-unsaturated compound.
Example
Acetaldehyde (CH₃CHO) undergoes aldol condensations in the presence of dilute NaOH.
Product formed: 3-hydroxybutanal (aldol), which on heating forms crotonaldehyde.
Why Dehydration Occurs
Dehydration occurs because the resulting α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound is more stable due to conjugation.
Types
- Self Aldol Condensation
- Crossed Aldol Condensation
Aldol vs Crossed Aldol Condensations
| Aldol Condensations | Crossed Aldol Condensations |
|---|---|
| Same carbonyl compounds react | Different carbonyl compounds react |
| Single major product | Multiple products possible |
| More predictable | Less predictable |
Limitations of Aldol Condensation
- Compounds without α-hydrogen do not undergo aldol condensations
- Crossed aldol reactions give mixtures
Importance for Class 12 & NEET
Aldol Condensations is frequently asked in:
- Reaction mechanism questions
- Product prediction
- Reason-based MCQs
MCQs
Q1. Which compound does not undergo aldol condensations?
- A. Acetaldehyde
- B. Acetone
- C. Benzaldehyde ✅
- D. Propanal
Answer: Benzaldehyde has no α-hydrogen.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why α-hydrogen is necessary?
α-hydrogen is required to form the enolate ion, which acts as the nucleophile.
Is aldol condensations reversible?
Formation of aldol is reversible, but dehydration makes it irreversible.
nucleophilic addition reactions
