Entropy and Spontaneity
In thermodynamics, entropy and spontaneity help us understand the direction and feasibility of natural processes. While energy is conserved in all transformations, the quality and disorder of that energy—measured by entropy—can change.
What is Entropy?
Entropy (S) is a measure of randomness, disorder, or the number of microscopic configurations (ways) in which a system can be arranged. It reflects the unavailability of a system’s energy to do work.
S = k × ln(W)
Where:
S = Entropy
k = Boltzmann constant (1.38 × 10⁻²³ J/K)
W = Number of microstates (arrangements)
💡 Insight: The greater the disorder or randomness, the higher the entropy. Gases have more entropy than liquids, and liquids have more entropy than solids.
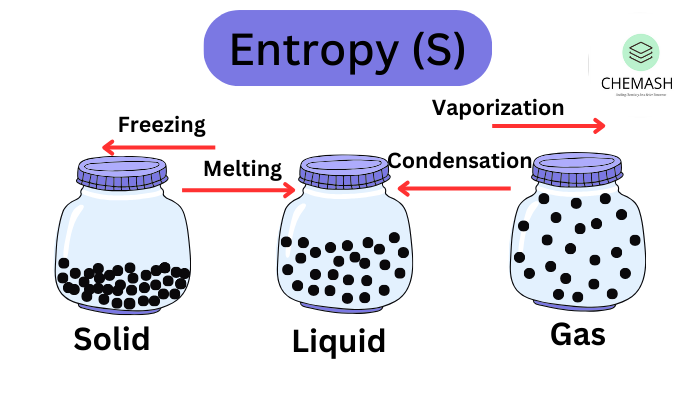
Entropy Change (ΔS)
- ΔS > 0: Increase in disorder (favorable)
- ΔS < 0: Decrease in disorder (less favorable)
Examples:
- Ice melting: ΔS > 0
- Water freezing: ΔS < 0
Spontaneity in Thermodynamics
A process is called spontaneous if it occurs naturally without continuous external influence. Example: ice melting at room temperature, rusting of iron.
Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity
ΔG = ΔH − TΔS
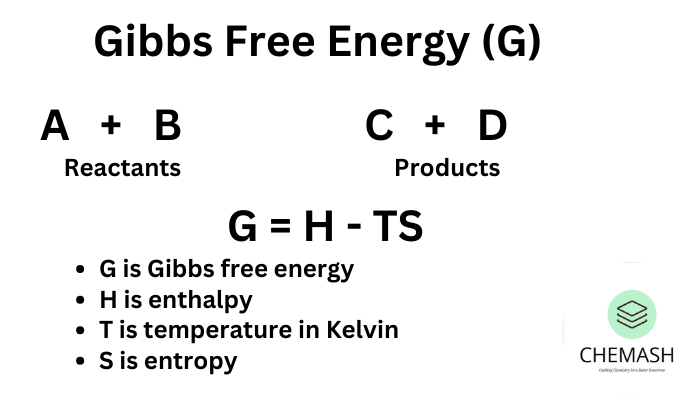
- ΔG < 0: Spontaneous
- ΔG > 0: Non-spontaneous
- ΔG = 0: Equilibrium
MCQs
- Which has the highest entropy?
a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Gas ✅
Explanation: Gas molecules move freely and have maximum randomness. - ΔG < 0 means:
a) Spontaneous ✅
b) Non-spontaneous
c) Equilibrium - If ΔS < 0, the process:
a) Increases disorder
b) Decreases disorder ✅
Explanation: Negative ΔS means less randomness.
True / False
- Entropy is a measure of energy content. ❌ False – It measures disorder.
- Spontaneity means the process is fast. ❌ False – Speed is not implied.
- ΔG = 0 means equilibrium. ✅ True
Quick Quiz
- State the formula for entropy in statistical terms.
- Give one example of a spontaneous but slow process.
- When ΔS is positive and ΔH is negative, is the process spontaneous?
FAQs
What is entropy in thermodynamics?
Entropy is a measure of disorder or randomness in a system, indicating the number of possible arrangements of particles.
How does entropy relate to spontaneity?
A positive entropy change generally favors spontaneity, but the overall spontaneity depends on enthalpy and temperature too, via Gibbs free energy.

Pingback: Thermodynamic Equations and Functions - CHEMASH