Group 14: Carbon Family (Tetrels)
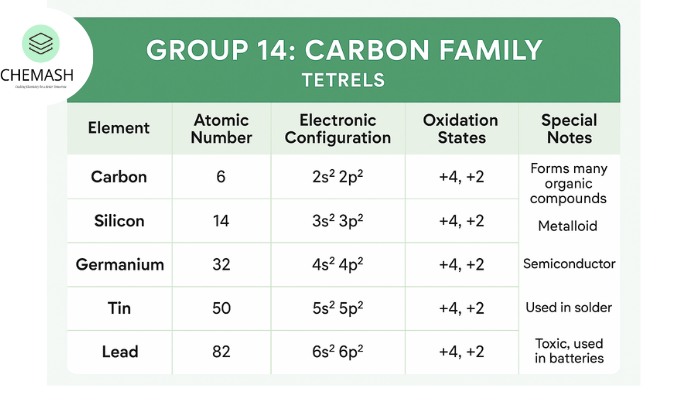
Group 14 of the periodic table, also known as the Carbon Family or Tetrels, consists of Carbon (C), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Tin (Sn), and Lead (Pb). These elements transition from non-metallic to metallic character down the group, making them crucial for periodic trends and chemical bonding. Learn more from Britannica: Carbon Group Elements.
Electronic Configuration and General Characteristics
The general outer electronic configuration is ns² np². This gives four valence electrons, enabling tetravalency.
- Carbon: Non-metal
- Silicon & Germanium: Metalloids
- Tin & Lead: Metals
Physical Properties
- Carbon shows allotropy: diamond, graphite, graphene.
- Melting and boiling points generally decrease down the group.
- Lead is the heaviest and densest element of the group.
- Carbon, silicon, germanium → semiconductors; tin, lead → conductors.
Chemical Properties
Common oxidation states: +4 and +2. The inert pair effect makes +2 more stable for heavier elements like Pb.
- Carbon: Hydrocarbons, carbonates, oxides.
- Si & Ge: Oxides, halides (+4 stable).
- Sn & Pb: Show +2 and +4; Pb prefers +2.
- Catenation: Carbon forms long chains → basis of organic chemistry.
Allotropes of Carbon
- Diamond: Hardest natural substance, thermal conductor.
- Graphite: Electrical conductor, lubricant.
- Graphene: Single-layer, extraordinary conductivity & strength.
- Fullerenes & CNTs: Applications in nanotechnology.
Compounds and Applications
- Carbon Compounds: Fuels, plastics, biomolecules.
- Silicon Dioxide: Sand, quartz, glass, ceramics.
- Germanium: Semiconductors, fiber optics.
- Tin: Tin plating, solder alloys.
- Lead: Batteries, radiation shielding (toxic, restricted use).
Trends in Group 14
- Atomic radius increases down the group.
- Metallic character increases.
- Electronegativity decreases.
- +4 oxidation state becomes less stable; +2 more stable for Pb.
MCQs: Test Your Knowledge
- General electronic configuration of Group 14 elements?
Answer: ns² np² - Name 3 allotropes of carbon.
Answer: Diamond, Graphite, Graphene - Which Group 14 element is widely used in semiconductors?
Answer: Silicon - Why does Pb prefer +2 oxidation state?
Answer: Inert pair effect - Which trend increases down the group?
Answer: Metallic character
FAQs
Q1: Why is carbon unique in Group 14?
Ans: It shows strong catenation and forms millions of organic compounds.
Q2: Which is the lightest and heaviest Group 14 element?
Ans: Carbon is the lightest, lead is the heaviest.
Q3: Why does metallic character increase down Group 14?
Ans: Due to larger atomic radius and weaker effective nuclear charge.
Q4: What is the industrial importance of silicon dioxide?
Ans: It is used in glass, cement, and electronics.
Next: Group 15: Nitrogen Family

Pingback: Nitrogen Family - CHEMASH