Group 15 Elements: Nitrogen Family (Pnictogens)
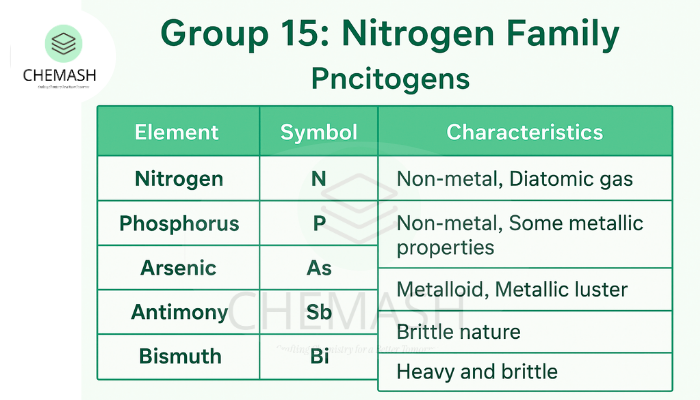
Group 15 of the periodic table is known as the Nitrogen Family or Pnictogens. This group includes Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), and Bismuth (Bi). The properties range from non-metallic (N, P) to metallic (Bi), with As and Sb being metalloids.
Electronic Configuration and General Characteristics of Group 15 Elements
The valence shell electronic configuration of Group 15 elements is ns² np³. Key features:
- Five valence electrons lead to oxidation states of -3, +3, and +5.
- Non-metallic to metallic character increases down the group.
- Show allotropy (e.g., white, red, and black phosphorus).
- Stable covalent bonding due to half-filled orbitals.
Physical Properties of Nitrogen Family Elements
- Nitrogen: A diatomic gas (N₂), 78% of atmosphere, colorless, odorless.
- Phosphorus: Allotropes include white (toxic, reactive), red (stable), and black (layered structure).
- Arsenic & Antimony: Metalloids with metallic luster, brittle nature.
- Bismuth: Heavy brittle metal, low thermal conductivity, used in alloys.
Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements
- Oxidation States: -3 (nitrides, phosphides), +3, and +5 in oxides and oxyacids.
- Hydrides: NH₃ (ammonia), PH₃ (phosphine), AsH₃, SbH₃, BiH₃ (stability decreases down the group).
- Oxides: Range from acidic (N₂O₅) to amphoteric (Sb₂O₃) to basic (Bi₂O₃).
- Reactivity: N₂ is inert (triple bond), P is reactive, As/Sb moderately reactive, Bi is metallic.
Important Compounds and Uses of Pnictogens
- Nitrogen: Used in fertilizers, ammonia (Haber process), proteins, nucleic acids.
- Phosphorus: Fertilizers, detergents, matches, pesticides.
- Arsenic: Semiconductors, wood preservatives (toxic, limited use).
- Antimony: Flame retardants, alloys, electronics.
- Bismuth: Cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, low-melting alloys.
Trends in Group 15 Elements
- Atomic size and metallic character increase down the group.
- Electronegativity decreases from N → Bi.
- Stability of +5 decreases, +3 increases.
- Hydride basicity decreases (NH₃ most basic, BiH₃ least).
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Group 15 Elements
- What is the electronic configuration of Group 15 elements?
- Why is nitrogen inert compared to phosphorus?
- Name two common allotropes of phosphorus.
- Which Group 15 element is a heavy brittle metal?
- Arrange NH₃, PH₃, AsH₃ in order of decreasing stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are Group 15 elements called?
They are called the Nitrogen Family or Pnictogens.
2. What is the valence electron configuration?
The configuration is ns² np³, with 5 valence electrons.
3. Which Group 15 element is most abundant?
Nitrogen, forming about 78% of Earth’s atmosphere.
Further Reading
Group 14: Carbon Family
Byju’s: Group 15 Elements
