Oxidation and Reduction
Oxidation and Reduction are fundamental chemical processes that involve the transfer of electrons. Together these processes are called Redox reactions (Reduction–Oxidation reactions). They are essential in many chemical, biological, and industrial processes.
Published: Sep 29, 2025 • Category: Redox Reactions
Oxidation
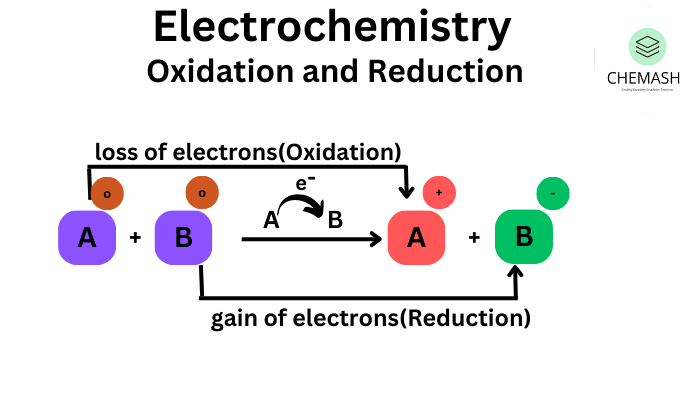
Oxidation is the process in which an atom or ion loses electrons, resulting in an increase in oxidation number.
- Loss of electrons
- Increase in oxidation number
- Addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen
- Example:
Fe → Fe2+ + 2e-
Reduction
Reduction is the process in which an atom or ion gains electrons, resulting in a decrease in oxidation number.
- Gain of electrons
- Decrease in oxidation number
- Addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen
- Example:
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
Redox Reaction
A reaction where both oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously is called a redox reaction.
Example:
Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu (Zn is oxidized, Cu²⁺ is reduced)
Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
- Oxidizing agent: Causes oxidation; it itself gets reduced. (e.g., KMnO₄, Cl₂)
- Reducing agent: Causes reduction; it itself gets oxidized. (e.g., Zn, H₂)
Daily Life Examples
- Rusting of iron (oxidation)
- Photosynthesis (reduction of CO₂)
- Respiration (oxidation of glucose)
- Batteries and electrochemical cells (redox basis)
Quick Quiz
- What is oxidation in terms of electron transfer? AnswerLoss of electrons.
- Give an example of a redox reaction. AnswerZn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu.
- What is the role of a reducing agent? AnswerIt donates electrons and gets oxidized.
- Is hydrogen gain oxidation or reduction? AnswerReduction.
- Which agent gets reduced in a redox reaction? AnswerThe oxidizing agent.
MCQs
- Which of the following is an oxidation reaction?
a) Gain of hydrogen
b) Loss of oxygen
c) Loss of electrons
d) Decrease in oxidation number Correct: c) Loss of electrons - Reduction involves:
a) Loss of electrons
b) Gain of oxygen
c) Gain of electrons
d) Increase in oxidation number Correct: c) Gain of electrons - Which is a reducing agent?
a) Cl₂
b) H₂O
c) H₂
d) KMnO₄ Correct: c) H₂ - Oxidation number increases in:
a) Reduction
b) Oxidation
c) Neutralization
d) Precipitation Correct: b) Oxidation - Which of the following is a redox reaction?
a) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂O
b) Zn + HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
c) AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO₃
d) BaCl₂ + H₂SO₄ → BaSO₄ + HCl Correct: b) Zn + HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
FAQs
How do I assign oxidation numbers?
Follow standard rules: element in free state = 0, oxygen usually −2, hydrogen usually +1, sum of oxidation numbers equals net charge.
Can a species be both oxidized and reduced?
Yes — in disproportionation reactions a species undergoes simultaneous oxidation and reduction.
Why are redox reactions important?
They power batteries, metabolic processes (respiration), photosynthesis, corrosion, and many industrial processes.
