Quantum Numbers
Quantum numbers are values that describe electrons in atoms. They provide details about an electron’s location, energy, orientation, and spin. Each electron has a unique set of four quantum number derived from the Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom. Understanding quantum number is essential for electronic configuration and quantum mechanics.
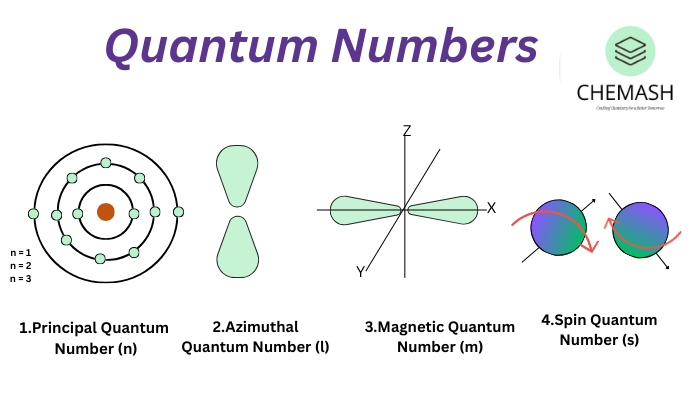
Types of Quantum Numbers
- Magnetic Quantum Number (m): Orientation of orbital in space. Range: –l to +l.
- Principal Quantum Number (n): Indicates the main energy level or shell. It can be 1, 2, 3 … Larger n means higher energy and larger orbitals.
- Azimuthal Quantum Number (l): Defines orbital shape. Values: 0 to (n–1).
l = 0 (s), l = 1 (p), l = 2 (d), l = 3 (f) - Spin Quantum Number (s): Electron spin direction, +½ or –½.
Summary Table
| Quantum Number | Symbol | Significance | Possible Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Principal | n | Main energy level | 1, 2, 3… |
| Azimuthal | l | Orbital shape | 0 to n–1 |
| Magnetic | m | Orbital orientation | –l to +l |
| Spin | s | Electron spin | +½, –½ |
Figure: Relationship between quantum numbers and orbitals
MCQs
- Which quantum number defines the size of an orbital?
Answer: Principal quantum number (n). - If n = 3, what are possible values of l?
Answer: 0, 1, 2. - For l = 2, how many orientations are possible?
Answer: 5 (m = –2, –1, 0, +1, +2). - Which quantum number shows electron spin?
Answer: Spin quantum number (s). - Can two electrons have same four quantum number?
Answer: No, due to Pauli Exclusion Principle.
FAQs
Q1: What are quantum number?
A: They describe an electron’s energy, shape, orientation, and spin.
Q2: How many quantum number exist?
A: Four — n, l, m, s.
Q3: Why are they important?
A: They explain electron configuration and chemical behavior.
Next, explore Electronic Configuration to see how quantum numbers arrange electrons in atoms.
