Introduction to States of Matter
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Furthermore, it exists in different physical states depending on temperature, pressure, and molecular interactions. The most commonly recognized states are solid, liquid, and gas; however, plasma and Bose-Einstein condensates also play a crucial role in advanced physics.
Table of Contents
Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT)
Physical States of Matter
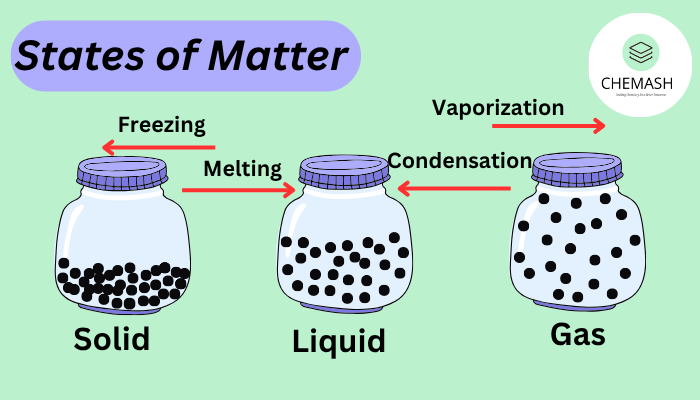
There are five known states of matter. In chemistry, we focus mainly on the first three.
- Solid: Particles are tightly packed with fixed positions and vibrate slightly. Consequently, solids maintain a definite shape.
- Liquid: Particles are closely packed but move around each other, giving liquids a definite volume but not a fixed shape.
- Gas: Particles are far apart and move randomly. As a result, gases have neither fixed shape nor fixed volume.
- Plasma: Ionized gas with high energy, commonly found in stars and lightning.
- Bose-Einstein Condensate: Formed at near absolute zero temperatures where particles merge into a single quantum state.
Key Characteristics of States
| Property | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Definite | Not definite | Not definite |
| Volume | Definite | Definite | Not definite |
| Compressibility | Negligible | Low | High |
| Interparticle Forces | Strong | Moderate | Weak |
Interconversion of States
States of matter change when we alter temperature or pressure. Key processes include:
- Melting: Solid → Liquid (upon heating)
- Freezing: Liquid → Solid (upon cooling)
- Vaporization: Liquid → Gas (upon heating)
- Condensation: Gas → Liquid (upon cooling)
- Sublimation: Solid → Gas directly; for example, camphor or dry ice.
Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT)
The kinetic molecular theory explains the behavior of gases. Its main principles are as follows:
- Gases consist of a large number of tiny particles.
- These particles do not exert attractive or repulsive forces on each other.
- Particles move constantly and collide elastically.
- The average kinetic energy of particles is directly proportional to temperature (Kelvin).
Quiz
- Which state of matter has no definite shape or volume?
a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Gas
d) Plasma
Answer: c)
Explanation: Gases expand or compress to fill any container; therefore, they have no fixed shape or volume. - Which process changes a solid directly into gas?
a) Evaporation
b) Condensation
c) Sublimation
d) Melting
Answer: c)
Explanation: Sublimation transitions solid → gas directly without forming liquid. - Which is NOT a characteristic of solids?
a) High compressibility
b) Definite shape
c) Strong forces
d) Fixed volume
Answer: a)
Explanation: Solids are almost incompressible because particles are tightly packed.
FAQs
Q1: What is plasma and where is it found?
A: Plasma is an ionized gas present in stars, lightning, and neon signs.
Q2: What is a Bose-Einstein Condensate?
A: A Bose-Einstein Condensate is a state of matter at near absolute zero where particles act as a single quantum entity.
Q3: Can liquids be compressed?
A: Liquids have low compressibility because particles are closely packed.
Next Topic: Ideal Gas Law → Explore the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and moles.
References: IUPAC
