Biochemistry: Definition, Scope, Biomolecules & Applications
Biochemistry is the branch of science that studies the chemical composition, structure, and reactions occurring within living organisms. It explains life at the molecular level by integrating principles of chemistry and biology.
Table of Contents
What is Biochemistry?
Biochemistry deals with the study of chemical substances and biochemical reactions that occur in plants, animals, and microorganisms. It focuses on understanding how biological molecules interact to maintain life.
Importance
- Explains cellular functions at molecular level
- Helps understand diseases and medical treatments
- Essential for biotechnology and genetic engineering
- Supports pharmaceutical and healthcare industries
- Improves agriculture and food production
Branches
| Branch | Description |
|---|---|
| Structural Biochemistry | Study of molecular structure of biomolecules |
| Enzymology | Study of enzymes and catalysis |
| Metabolic Biochemistry | Study of metabolic pathways |
| Clinical Biochemistry | Application in diagnosis of diseases |
Biomolecules
Biomolecules are organic molecules essential for life. They are broadly classified into four major groups:
1. Carbohydrates
Primary source of energy. Examples: glucose, starch, cellulose.
2. Proteins
Composed of amino acids. Perform structural, enzymatic, and regulatory roles.
3. Lipids
Hydrophobic molecules used for energy storage and membrane structure.
4. Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA store and transmit genetic information.
Enzymes
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed.
- Highly specific in action
- Reusable
- Affected by temperature and pH
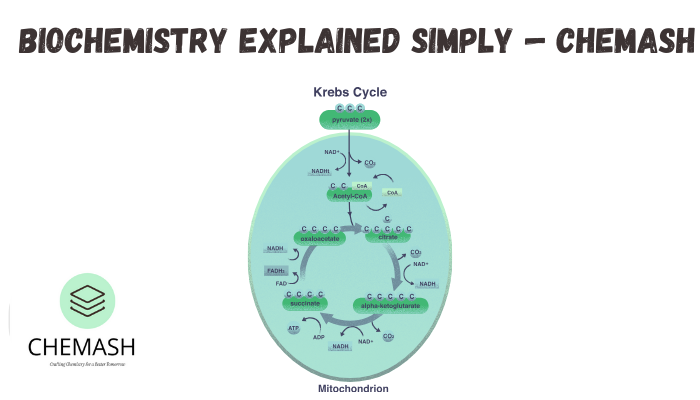
Metabolism
Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions occurring in living organisms.
- Anabolism: Building reactions
- Catabolism: Breaking reactions
Applications
- Medicine and diagnostics
- Pharmaceutical development
- Genetic engineering
- Food and nutrition science
- Environmental science
MCQs
- biochemistry mainly deals with:
A. Physical laws
B. Chemical reactions in living organisms
C. Atomic structure
D. Nuclear reactions Answer: B - Which biomolecule stores genetic information?
A. Protein
B. Lipid
C. Carbohydrate
D. Nucleic acid Answer: D
Frequently Asked Questions
Is biochemistry a part of chemistry or biology?
It is an interdisciplinary science combining both chemistry and biology.
What are the career options in biochemistry?
Careers include medical research, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and academia.
Why is biochemistry important in medicine?
It helps understand disease mechanisms and drug action at molecular level.
- Biomolecules: Classification and Functions
- Enzymes and Biological Catalysis
- Metabolism: Anabolism and Catabolism
- Proteins: Structure, Properties and Functions
- Carbohydrates: Types and Biological Role
- Lipids: Structure and Biological Importance
- Nucleic Acids: DNA, RNA and Genetic Information
